Undoubtedly, one of the trends in health technology in 2021 is the consolidation of healthtechs. These startups have spread widely in recent years. Since 2014, they sum up US$ 430 million in investments, according to the survey Healthtech Report Brazil 2020.
Basically, these businesses are aimed at solving problems in healthcare services. They offer innovative solutions that improve both access to healthcare and the quality of life of patients. Innovations range from Artificial Intelligence (AI) diagnostic systems to digital medicine.
Moreover, they operate in the optimized management of public health entities, in smart clinics and offices, in self-service and self-care services and offer cutting-edge technologies for clinical and laboratory examinations.
Learn about how healthtechs work the importance of such segment and some of their solutions that have been revolutionizing health.
Healthtechs: what are they?
First, let’s better understand what a startup is: an innovative company with a repeatable and scalable business model in a scenario of uncertainties. That is: a business model that generates value, but without the certainty that the project will actually work or be sustainable; it can deliver the same product or service on a large scale without many adaptations; and grow more and more in revenue at the same time as costs slowly rise.
To do this, they use cutting-edge technologies such as Artificial Intelligence (AI), machine learning, big data and robotics, inter alia.
Undoubtedly, one of the main advantages of startups is the speed with which they create disruptive products and services. That is, they transform the market and deliver more value to the consumer.
By the way, these are the characteristics that differentiate them from conventional companies, in which any change needs to go through a slower internal process.
So, briefly, healthtechs are the name given to health startups. In English, health means healthcare services and tech, technology. In recent years, the suffix tech has been increasingly used to designate startups.
Importance of healthtechs for health
In Brazil, the lack of access to quality healthcare affects millions of people. Many live in places without basic infrastructure, such as specialists, exams, treatments and medicines, for example.
In this scenario, healthtechs help democratize health by seeking solutions to these bottlenecks. According to Global Health Care Outlook Survey , conducted by Deloitte, these startups are helping solve some healthcare services challenges, such as faster digital adherence; reduction of treatment costs due to the agility and accuracy of examinations and diagnoses; and regulation and compliance, through more effective cost and resource management.
- Nowadays, we can say that healthtechs serve the main areas below:
- Preventive medicine: prevent or slow the progression of diseases;
- Predictive medicine: detect the predisposition of certain diseases;
- Proactive medicine: close doctor-patient relationship, supported by technology;
- Personalized medicine: using data to personalize treatments;
- Medical management: automation and data analysis to optimize processes in hospitals, clinics, offices and laboratories.
Solutions developed by healthtechs
In fact, healthtechs offer services that benefit patients and help doctors and health institutions on a daily basis. Learn about some solutions that made positive changes in the industry:
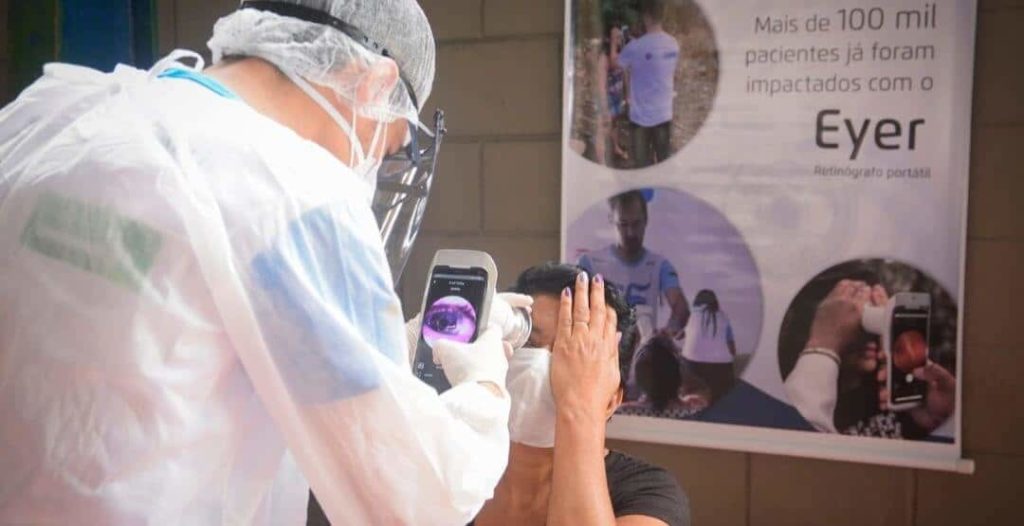
Accessibility and quick fundus and refraction exams and diagnoses.
In-office, the fundus camera provides a quicker acess to patients’ fundus images. The specialist can diagnose early, start treatment and monitor various diseases, such as glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy and age-related macular degeneration (AMD).
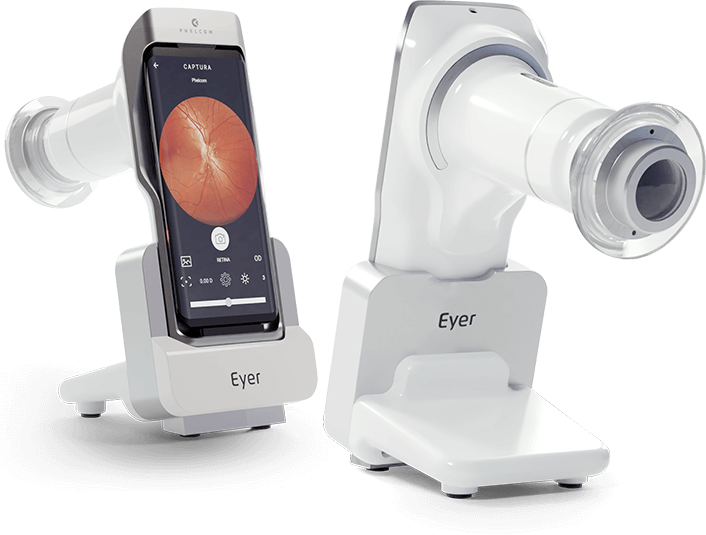
However, the high cost of the equipment – with models of up to BRL100,000 – can make a purchase inviable. The startup Phelcom Technologies created the smartdevice Eyer to solve this problem.
Coupled to a smartphone, the technology captures high-quality images from the eye fundus and sends them to an online platform, Eyer Cloud. It enables making exam reports, filing a patient’s history and other features.
Price adds an advantage: the equipment is up to 4 times cheaper than a conventional retinograph.
On its turn, startup EyeNetra offers the Mobile Refraction Kit. It can run a vision test through virtual reality. In the end, the technology measures degrees of myopia, astigmatism or hyperopia and prescribes the glasses, which will need the final approval of an ophthalmologist.
More than this, there are products to check the accuracy of the measured degrees and a set of physical lens to evaluate and validate the first test results. Finally, the company also offers a set of software to collect and store all this data for the experts to review.

Machine learning detects disease patterns
More than remote diagnosis, some remote reporting software work with the principle of machine learning. Basically, it collects data, learns from it and improves automatically. It does not necessarily require programming.
In diagnostic medicine, the tool evaluates an extensive database of patients’ symptoms to find patterns for each disease. This way it cheks for a disease in an individual, based on traits presented.
Some systems are available in Brazil. For example, the system Portal Telemedicina analytically compares face-to-face scans to similar cases from a database of 30 million images and scans. The platform provides medical recommendations based on reliable and accurate criteria.
If the medical exam and the algorithm recommendation do not match, it forwards the exam to three other specialists for further evaluation. In addition, the program learns from each report issued, collecting clinical repertoire to its database.
Another innovative aspect is the automatic exam screening, which prioritizes emergency cases in the doctor’s queue.
It is worth noting that data privacy, one of the current challenges of artificial intelligence, is a field of study of the scientific community. In this sense goes the concept of federated learning, which circulates only algorithms and not patient information. This allows multiple locations to share results and improve algorithms.
Accurate diagnosis of breast cancer
Imagine accurately identifying the area of the breast with a suspected change and, on top of that, easing the biopsy? Some artificial intelligence softwares are able to detect breast cancer more precisely.
One of them can even predict unusual image patterns in a mammography and point out the area that requires further investigation. The algorithm was created by Dasa in partnership with CureMetrix, an American startup.
Another software, developed by Google, may be a “second medical opinion” about mammography. The algorithm presented 11.5% more accuracy compared to human analysis.
However, humans show the same result as the machine when two doctors evaluate the exam. Since it is common that two experts analyze the image, Google’s tool can be the “second expert”.
Predicting breast cancer growth and metastasis
EndoPredict genetical test measures the high or low chance of breast cancer spreading to other parts of the body for the next ten years. It avoided chemotherapy in 70% of patients with negative nodules in clinical studies.
However, testing is recommended only for recent disease diagnoses, at early stages , with positive for estrogen receptors and negative for HER2 protein.
The Computer Science and Artificial Intelligence Laboratory (CSAIL) at MIT and Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), from the United States, created a new machine learning model. It can predict, from a mammography, whether a patient will develop breast cancer within five years.
With more than 90,000 exam evaluations in the database, the Artificial Intelligence (AI) has learned the subtle patterns in breast tissue that are harbingers of malignant tumors.
The team’s model was significantly better at predicting risk than the existing approaches. It accurately positioned 31% of all cancer patients in their highest risk category, compared to only 18% of traditional models.
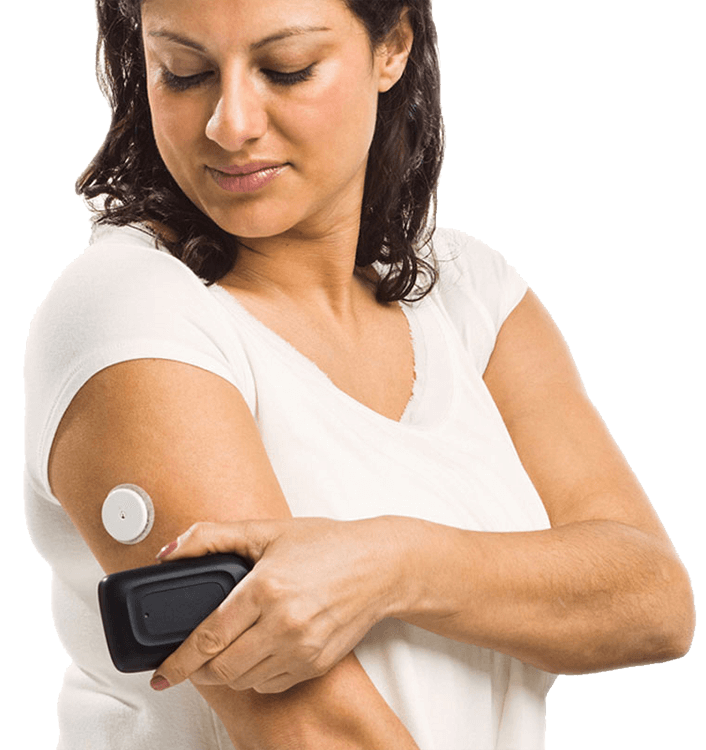
Technology helps monitoring diabetes
Imagine checking the glucose rate only by reading a small sensor installed on the back of the arm? With the help of a mobile-like device, the patient tracks the blood glucose levels on the screen without having to stick his fingers several times a day.
Instead of analyzing a drop of blood, as usual, the technology uses the interstitial fluid under the arm to capture the amount of glucose without having to pierce the tissue collect fluid around the vessels.
Moreover, the device checks levels 16 times a day and predicts rises or falls of glucose in the following hours. Thus, it helps to avoid hyper and hypoglycemia.
The technology also allows the user to scan the captured information every eight hours. It remains stored on the device itself or is accessible by the app. Data may be available to the doctor via cloud storage. This way, the expert doctor follows the patient conditions real time and decides for eventual changes in treatment, if necessary.
Another advantage is the possibility to share data with others, such as parents and caregivers. Thus, it is even safer to control diabetes.
Other innovations are the insulin pumps with continuous glucose monitoring, which allow the doctor to determine the exact amounts that should be released to the patient’s blood. Also the inhalable insulin, sold in powder cartridges with three sizes of dosages. The patient inserts the cartridge into an inhaler and, while aspirating, takes the substance to the lung, which is absorbed into the bloodstream. Therefore, it reduces blood glucose levels.
Telemedicine systems: from online consultations to process management
The expansion of telemedicine in Brazil, since last year, has made many clinics and offices look for technologies. The market has several healthtechs that offer complete and innovative telemedicine systems.
Services range from online appointments, remote diagnosis and prescription issuance to electronic medical records, online appointment scheduling and stock control.
Conclusion
We are approximately 7.8 billion people worldwide. Many live in countries with poor access to healthcare. In this sense, it is essential to invest in affordable solutions, in terms of space and cost, which help prevention, treatment and healthcare support.
The healthtechs have come and are committed to such proposal. Their main goal is to improve the people’s quality of life.
Reviewed by Paulo Schor, ophthalmologist, free professor and director of innovation of the Federal University of São Paulo (Unifesp) and collaborator of the Faculty of Medicine of the Albert Einstein Hospital.
Learn more about health technology on the Phelcom blog.