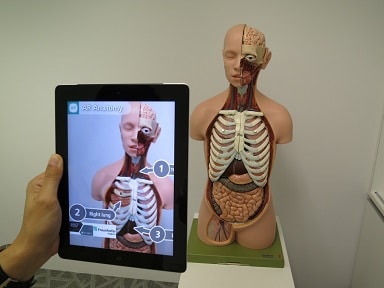
In real time, the technology shows the material world overlayed with computer-made images, enabling greatly improved composite observations.
For this, smartphone cameras, tablets, smart glasses and even state-of-the-art helmets are used, so that the hands are unnecessary to command interfaces in systems and applications.
For instance, there is a strong trend to use Augmented Reality (AR) in this industry, according to the Journal of Med Internet Research (JMIR). Even with a still low use by doctors and institutions, there is an increasing number of applications of AR in medicine.
Learn about the advantages of using augmented reality in health and some cases of success.
Augmented reality X Virtual Reality
First, it’s important to understand the difference between augmented reality and Virtual Reality (VR).
VR is a computer-simulated environment that provides visual, sound and even tactile effects to the user. It allows complete immersion in the virtual scenario, as if the person was actually present there. For this, it uses technologies with stereoscopic displays, such as the popular headsets (special glasses that transmit the simulation).
AR, in its turn, integrates the physical and the virtual by overlaying computerized images in the real world, through software and devices. For example, the Google Glass app can be accessed from the user’s own mobile phone or tablet. There is also the famous game Pokémon Go, in which players searched for virtual Pokémon in real-world environments using the mobile phone camera.
Augmented reality in healthcare: advantages
Undoubtedly, there are numerous advantages of using AR in health. One of them is to ease access to the patient’s medical history in emergencies or on the surgery table, for example. Image overlaying may also more accurately ensure to locate an area of interest in surgical procedures, thus decreasing risk to the patient. In this case, it is possible to integrate imaging examinations and better see every detail of the organs in the preoperative care and, thus, have more success in surgery.
In fact, technology is a great ally of telemedicine. For example, specialists can instruct other doctors remotely in more complex operations. Another aspect is diagnostic medicine, because the patient can better understand the diagnosis and the recommended treatment.
AR has also been used in the digital screening of patients who have suffered accidents. In these cases, orthopedists help in the performance of arthroscopic surgeries on shoulders and in training interns and residents to carry out ultrasound examination at the care site.
Neurosurgery is one of the most advanced specialties in the use of AR, with reports of tumor resection, open neuro-vascular surgeries, spinal procedures, location of catheters or probes, cortical resection in epilepsy and aneurysms involving unusual trajectories or hidden ramifications.
In hospitals and clinics, the technology assists remote support by enabling on-site technicians and teams to receive specialized help needed for installation, setup, maintenance, troubleshooting, and repair of sensitive and specialized hospital equipment.
Teaching in medicine
Augmented Reality in healthcare allows seeing details of the human body and training procedures in a repetitive and precise way.
Student, imagine practicing surgery in a virtual environment? Stanford University has a simulator which allows the most complete training for the future surgeon.
For researchers, a three-dimensional virtual surgical environment can allow for enhanced preoperative planning and testing. It thus improves patient results, decreases complication rates and improves technical skills.
The Stanford Virtual Surgical Environment (VSE) is developed for rhinologic procedures. The technology allows the surgeon to interact with patient-specific three-dimensional reconstructions of nasal sinus CT data sets using a modified haptic interface device, triggering a virtual endoscope.
In Brazil, there are also options for simulators. For example, Eyesi is aimed at training intraocular cataract surgery and vitreo-retinal procedures. It presents performance score and evaluates tremor, movement accuracy and repetitiveness, among other analyzes. Thus, it is a good tool for resident practice to introduce new techniques in ophthalmic surgery.
There are also the da Vinci surgical systems for robotic surgery, already in the fourth generation. The technology carries out minimally invasive surgeries in different procedures. One of its tools is a console – inspired by flight simulators – in which doctors visualize the high-definition 3D images and make the operative movements with their own hands, which are transmitted to the robot.
Another application is training and retraining for students, residents and specialists in care or in the surgical center. Thus, it is possible to carry out an ethnographic analysis of the performance of the professional, who is alone during the procedure, through the capture of images by a camera installed on the site.
Augmented Reality solutions in healthcare
On the market, there are already quite interesting solutions of AR.
For example, the application EyeDecide allows you to see the eyeball from any angle just by directly touching the image generated on the tablet and rotating it with your finger. It is also possible to reduce, expand, move or make notes on the eye in almost any direction. All this assists to simulate various disorders and helps to diagnose more accurately.
The app Anatomy 4D makes it possible to explore more than two thousand anatomical structures. Undoubtedly, it helps students and medical colleges.
Even with all the advantages, augmented reality in health is still relatively new and is not heavily employed in the area. However, as it proves its value for the quality of patient care, soon AR technologies will be stronger in the medical industry.
Reviewed by Paulo Schor, ophthalmologist, associate professor and director of innovation of the Federal University of São Paulo (Unifesp) and collaborator of the Faculty of Medicine of the Albert Einstein Hospital.
Follow Phelcom blog and learn more about augmented reality in healthcare.